What Do You Know About
ArchaeOLogy?
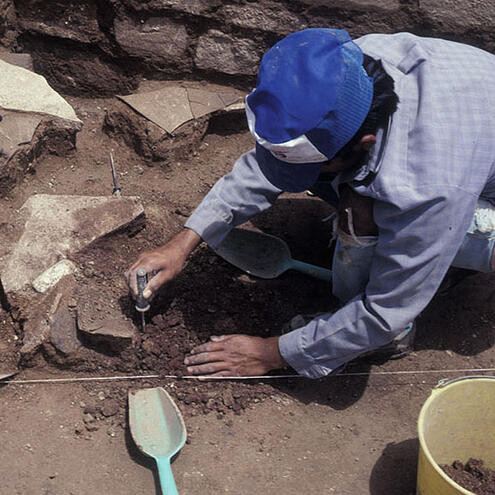

Archaeology is the study of:
fossils
past cultures
ancient documents
ANSWER: past cultures
Archaeology is an important tool for solving the mysteries of ancient life. It builds a picture of how people lived in the past from the material clues they left behind.
You can do archaeology:
only underwater
only in the ancient Inca city of Huanuco Pampa
anywhere
ANSWER: anywhere
From the scorching deserts of Egypt to the deep icy water of the Arctic, archaeologists can work anywhere!
Why do archaeologists create a map of the site before they dig?
to claim possession of the land
to find out where they want to dig
to locate buried treasure
ANSWER: to find out where they want to dig
Before archaeologists start digging, they need to know where to dig—and it can't just be anywhere. They use a survey map to locate the best places to excavate, where they have the best chance of finding evidence to address their questions.
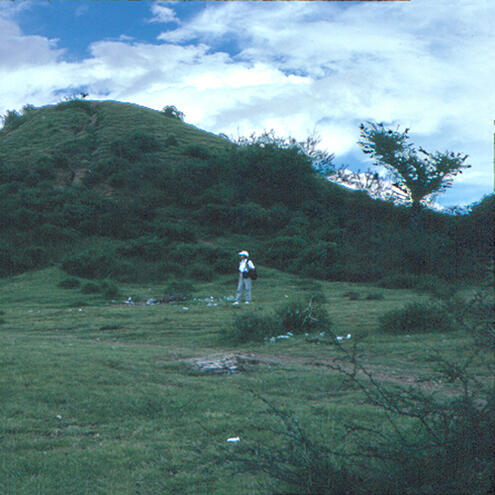

What is the best strategy for excavating an archaeological site?
shut your eyes, throw a coin, and start digging wherever the coin lands
pick an area based on a site map and divide it up into a grid pattern
dig from one end to another until you find something good
ANSWER: pick an area based on a site map and divide it up into a grid pattern
Most archaeological sites are very large—some even as big as a city. So it would take too much time and be too expensive to excavate the entire site. Archaeologists don't dig in random locations; they excavate a site in an organized way by dividing it into a checkerboard-like pattern.
Archaeologists look for different soil layers that they identify by color and texture. If the layers haven't been disturbed, what can they tell us?
artifacts found in the same layer are about the same age
artifacts found in a lower layer are younger
they tell us where artifacts were made
ANSWER: artifacts found in the same layer are about the same age
Over time, new layers of soil build up. Usually the further down you dig, the older the layer of soil. This is useful information—objects found in the same layer in different areas of the site might be roughly the same age.
What kinds of tools do archaeologists use?
ground penetrating radar, aerial photography, and submarines
dental pick, shovel, and tape measure
all of the above
ANSWER: all of the above
Archaeologists use a combination of high- and low-tech tools. Often simple tools like a trowel and a paintbrush are the most appropriate for excavation. New technologies like remote sensing and x-rays give archaeologists a new way to find suitable places to dig.
What are some of the most common objects found on an archaeological site?
old clothes
broken pieces of pottery
dried food
ANSWER: broken pieces of pottery
Pottery can survive for a really long time in most conditions because it does not decompose easily. Objects made of leather, wood, bone, and cloth are less likely to be found.
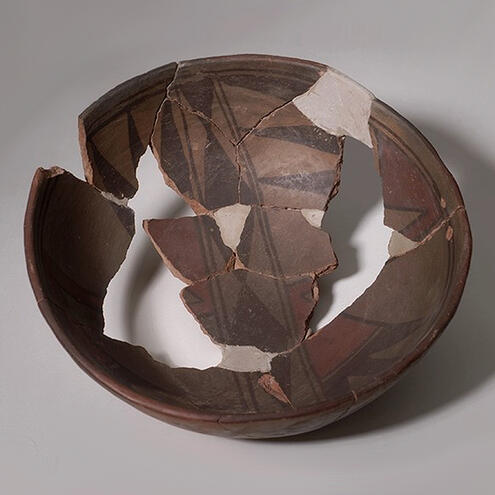

Imagine you're an archaeologist studying this object. What would you have a hard time figuring out?
how old it is
what it was used for
why it broke
ANSWER: why it broke
Archaeologists can use tools such as carbon dating to analyze how old an object is. By observing its shape, size, and decoration, they can also try to understand what an artifact was used for. But they can't look into the past to see why it broke.

What do archaeologists usually do with the objects they find?
sell them on the Internet
bury them again where they were found
study them in a lab in the country where they found them
ANSWER: study them in a lab in the country where they found them
Archaeologists store artifacts in a lab or museum in the country where they were found. This way, they can spend the next weeks, months, or even years analyzing them. If new technologies are invented in the future, archaeologists can come back and take another look.
How do archaeologists spend most of their time?
they search for lost treasure
they study objects and analyze data in the lab
they look for new sites
ANSWER: they study objects and analyze data in the lab
Many archaeologists only spend a few months in the field each year. They spend even more time planning for an excavation and researching in the lab.
You might also like...
Image Credits:
Photos: site excavation: courtesy of Chuck Spencer; Oaxaca, Mexico: courtesy of Christina Elson; pottery shards: courtesy of AMNH; bracelet: courtesy of AMNH



 Biodiversity
Biodiversity
 Brain
Brain
 Genetics
Genetics
 Marine BiOLogy
Marine BiOLogy
 MicrobiOLogy
MicrobiOLogy
 PaleontOLogy
PaleontOLogy
 ZoOLogy
ZoOLogy
 AnthropOLogy
AnthropOLogy
 ArchaeOLogy
ArchaeOLogy
 Astronomy
Astronomy
 Climate Change
Climate Change
 Earth
Earth
 Physics
Physics
 Water
Water
