Tuning the Telescope
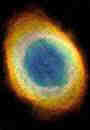
The Hubble Space Telescope was launched on April 25,1990 by the Space Shuttle Discovery. Soon afterwards, scientists discovered that its vision was blurred by a defect in the 94-inch, 1,800-pound mirror at the heart of the telescope. They used computers to compensate for the flaw until 1993, when astronauts flew up to the orbiting telescope and fixed the problem with high-tech mirrors. Like any other tool, the Hubble needs regular maintenance. Missions in 1997 and 1999 replaced old gyroscopes, upgraded computer systems, patched insulation blankets, and added new stargazing equipment—including infrared and ultraviolet cameras. The Hubble has since gone on to observe many of the most fantastic events in the cosmos, including the famous Ring Nebula, seen at right.
Size: 43 feet long
Weight: 25,000 pounds
Launched: April 25, 1990
Intended lifetime: at least 15 years
Use: scientists from around the world schedule time to use this tool
Speed: 17,000 miles per hour
Significance: the Hubble Space Telescope is the largest space telescope ever launched; it gives astronomers the clearest views of deep space
The Hubble Space Telescope is one of the best telescopes in the world because it:
is outside Earth's atmosphere
has the biggest mirror
took lots of photography classes
Correct!
The Hubble Telescope takes an image 10 to 20 times better—depending on atmospheric conditions—than typical large, ground-based telescopes, even though the Hubble is only a medium-sized telescope.
Meteorites come from:
anywhere in the universe
just Mars
anywhere in our solar system
Correct!
Meteorites come from our own solar system. In fact, most come from the asteroid belt, a ring of rocks and debris between Mars and Jupiter.
In over ten years in orbit, the Hubble Space Telescope has circled Earth over 50,000 times!
Fact
The Hubble has logged some 1.5 billion miles in its 58,400 orbits around Earth. That's like making eight round trips to the Sun!
The Hubble Space Telescope is the most powerful astronomical tool ever built. Its crystal-clear vision allows it to take the clearest pictures ever of planets, star clusters and galaxies.

Mike Shara, astrophysicist



 Biodiversity
Biodiversity
 Brain
Brain
 Genetics
Genetics
 Marine BiOLogy
Marine BiOLogy
 MicrobiOLogy
MicrobiOLogy
 PaleontOLogy
PaleontOLogy
 ZoOLogy
ZoOLogy
 AnthropOLogy
AnthropOLogy
 ArchaeOLogy
ArchaeOLogy
 Astronomy
Astronomy
 Climate Change
Climate Change
 Earth
Earth
 Physics
Physics
 Water
Water
