What Do You Know About the
UNIVERSE?
the further back in time we see
the further into the future we see
we see things that happened just recently
ANSWER: the further back in time we see
When we flip a switch we see the light almost instantly. But sunlight is 8 minutes old, and light from galaxies can be millions or even billions of years old! Light that is 13.8 billion light years away (13.8 billion ly old) has reached Earth from every direction. Astronomers call this sphere the observable universe.
What is the most distant thing in space that we can see without a telescope ?
the Orion Nebula, a stellar nursery in our Milky Way
the Andromeda galaxy, our closest neighbor
the Virgo cluster, a collection of about 2000 galaxies

ANSWER: the Andromeda galaxy, our closest neighbor
Andromeda is over 2.5 million light-years away. But compared to the size of the universe, that distance is tiny.
In the 1920s, Edwin Hubble and fellow astronomers at Mount Wilson Observatory were the first to discover galaxies beyond the Milky Way . What else did they discover?
distant galaxies move farther and farther away from us
distant galaxies look like the Milky Way
distant galaxies give off light
ANSWER: distant galaxies move farther and farther away from us
It seemed the universe was stretching or expanding. This was the first evidence for the Big Bang theory.
According to the Big Bang theory, the universe was born about 13.8 billion years ago. At the moment of the Big Bang, the universe was:
hot and dense like the center of a star
hot and dense like the center of Earth
scientists have no idea
ANSWER: hot and dense like the center of a star
The very early universe was very hot, very dense, and very bright, like the center of a star. Everywhere was starlight!
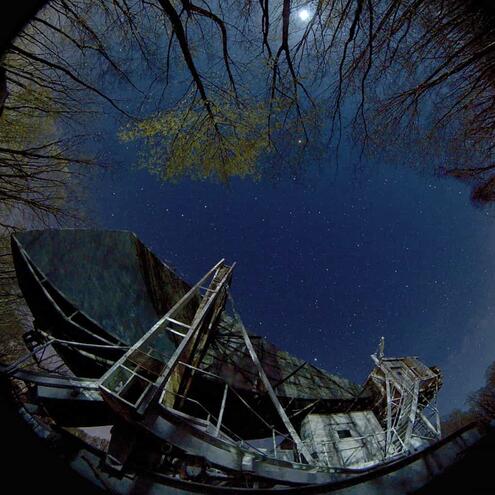

In 1964, astronomers working with a radio telescope in New Jersey accidentally discovered something that came to be known as the cosmic microwave background. What was it?
a bright white light from the Big Bang
low energy radiowaves from the Big Bang
a loud noise from the Big Bang explosion
ANSWER: low energy radiowaves from the Big Bang
The astronomers thought the faint signal might have been pigeon poop on their telescope. But they actually detected the afterglow of light from the early universe — the oldest light ever seen. Only a radio telescope could pick up the longer wavelengths of the cosmic microwave background.

In 2009, the Planck satellite was launched into space to measure light in the microwave band. It orbits:
the Moon
Earth
the Sun
ANSWER: the Sun
Planck orbits the Sun about 1.5 million km (1 million mi) from Earth, at a point where Earth and the Sun's gravity balance each other exactly. Their combined gravity means that anything near this location orbits the Sun in exactly one year, and stays in the same place relative to Earth.
Albert Einstein's famous equation E=mc2 shows the relationship been an object's mass (m) and its energy (E). What does 'c' represent?
temperature
the speed of light
gravity
ANSWER: the speed of light
The 'c' stands for the speed of light, or 670 million miles per hour. Since 670 million squared is a huge number, this means that an object with just a little mass holds a huge amount of energy! The letter 'c' comes from the Latin word celeritas, which means 'swiftness.'
Normal matter is everything we can touch and see, including dogs, trees, planets, stars, and galaxies. It makes up how much of the total mass-energy in our universe?
less than 5 percent
about 25 percent
more than 70 percent
ANSWER: less than 5 percent
More than 95% of the universe is made up of stuff we can't see; Dark matter, an invisible substance, makes up about 25%. A mysterious pressure called dark energy makes up about 70%.
Dark matter is invisible, so how do scientists know it exists?
its gravity affects stars and galaxies
it emits light in otherwise dark regions of space
it absorbs light like a black hole
ANSWER: its gravity affects stars and galaxies
We can't see dark matter because it does not emit or absorb light. Scientists know it's there because its gravity affects things we can see. Dark matter's gravity holds galaxies together.
How did dark energy get its name?
it's related to dark matter
light cannot escape it
astronomers don't know much about it
ANSWER: astronomers don't know much about it
In 1998, astronomers discovered that a mysterious pressure was working against gravity and causing the expansion of the universe to speed up, or accelerate. Scientists called it 'dark energy.'
You might also like...
Image Credits:
dark matter background image, © AMNH; Andromeda Galaxy, courtesy of NASA/JPL-Caltech; Bellhorn Telescope, © AMNH; Planck Satellite and Earth, courtesy of JPL/NASA; Albert Einstein, courtesy of AMNH.



 Biodiversity
Biodiversity
 Brain
Brain
 Genetics
Genetics
 Marine BiOLogy
Marine BiOLogy
 MicrobiOLogy
MicrobiOLogy
 PaleontOLogy
PaleontOLogy
 ZoOLogy
ZoOLogy
 AnthropOLogy
AnthropOLogy
 ArchaeOLogy
ArchaeOLogy
 Astronomy
Astronomy
 Climate Change
Climate Change
 Earth
Earth
 Physics
Physics
 Water
Water
