What Do You Know About Astronomy?
Take this quiz to find out!
In 1999, astronomers were able to calculate the approximate age of the universe. The number is:
about 4,000 years
about 13 billion years
about 900 billion years
ANSWER: about 13 billion years
Thanks to new data from telescopes on Earth and in space, astronomers were able to calculate more accurately than ever before how fast the universe is expanding. This measurement, in turn, tells us how much time has passed since the expansion first began—the moment of the Big Bang .

Stars and planets are shaped like spheres because:
gravity pulled them into that shape as they formed
they eroded into round shapes over millions of years
round shapes have less wind resistance
ANSWER: gravity pulled them into that shape as they formed
Gravity is a fundamental force in the universe that affects all matter. If enough matter gathers in one place, the matter will "self-gravitate" and pull itself into a spherical shape. That's why there are almost no square or triangular heavenly bodies.
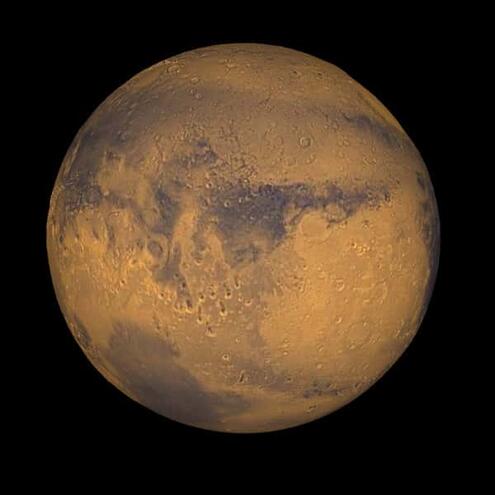
If you went looking for life in outer space, a good place to look would be

Mars, because it may have liquid water below its surface

Neptune, because it has weather systems like those on Earth

Uranus, because its blue-green surface looks as though it could sustain life
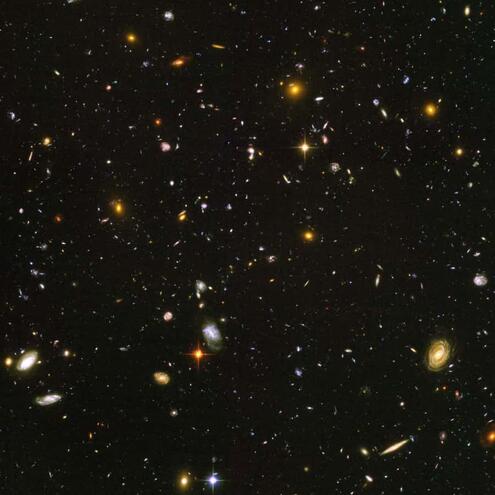

In this picture, almost every blob you see is:
a star
a planet
a galaxy
ANSWER: a galaxy
The area of the sky shown in the image is tiny: about the size of Abraham Lincoln's eye on a U.S. penny held at arm's length. It's like viewing a tiny part of the sky through a very long straw that reaches toward the end of the universe. This picture shows that there are many billions of galaxies in the cosmos beyond our own Milky Way Galaxy.
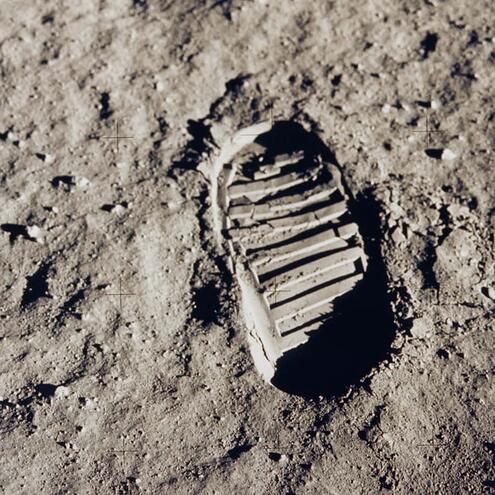

Humans walked on the Moon for the first time in July of 1969. How long will their footprints be visible on the Moon's surface?
windstorms have already erased them
hundreds of thousands of years
about fifty years
ANSWER: hundreds of thousands of years
On July 20, 1969, American astronauts walked on the Moon for the first time. Since there are no wind or water or life on the Moon to disturb them, their footprints will be around for a very long time.

For every evening star you can see from Earth, how many more stars in the Milky Way Galaxy remain unseen?
about 20 million
about 3,000
about 40
ANSWER: about 20 million
You can see about 5,000 stars in the Milky Way from Earth with the unaided eye. But for each one of those stars , there are over twenty million you can't see! There are about 100 billion stars in the Milky Way Galaxy , and almost all of them are too faint, too far away, or too blocked by cosmic dust to be seen without a telescope.

A comet's tail can stretch as long as:
about 10 miles
about 5,000 miles
hundreds of millions of miles
ANSWER: hundreds of millions of miles
Comets are often described as "dirty cosmic snowballs." They travel through the solar system , developing new tails of gas and dust each time their orbits bring them close to the Sun. These stream off into space from the side facing away from the Sun.
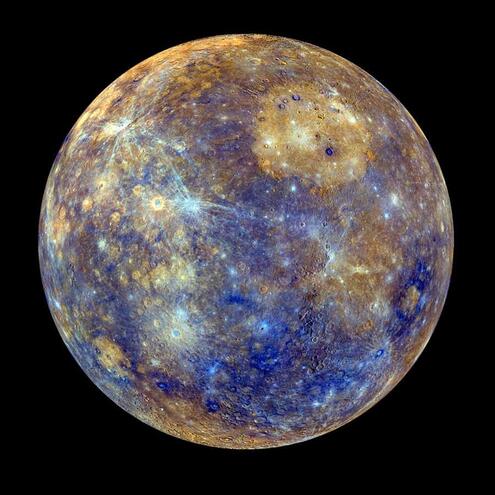

A "day" on the planet Mercury, from sunrise to sunset, lasts about:
six Earth hours
six Earth months
six Earth years
ANSWER: six Earth months
Mercury is the smallest planet and the closest to the Sun. Over billions of years, its gravitational interaction with the Sun has slowed its rotation rate so much that, when the Sun rises at any place on Mercury, it's about half an Earth-year later before it sets there. We learned a lot about Mercury from the Spacecraft Mariner 10, which photographed about half of Mercury's surface in the mid-1970s.

If your spaceship could travel at the speed of light, how long would you take to cross the entire Milky Way Galaxy?
about 10 years
about 1,000 years
about 100,000 years
ANSWER: about 100,000 years
The Milky Way Galaxy is a huge, pinwheel-shaped collection of stars, dust, and gas. The Sun is located on one of its spiral arms, about 25,000 light-years (150 quadrillion miles!) out from the center of our galaxy.
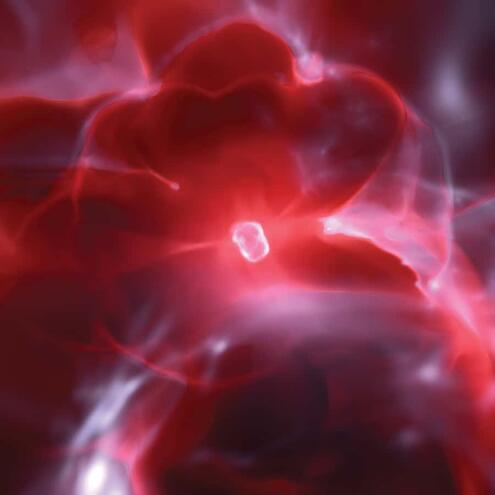

When a massive star finally dies, what happens?
it turns into a white dwarf
it explodes in a supernova
it becomes a planet
ANSWER: it explodes in a supernova
A low or intermediate mass star (like our Sun) shines for billions of years before it shrinks into a white dwarf. A massive star, however, will shine for only a few million years before blowing up in a giant explosion called a supernova. The blast hurls the star's remaining matter across space , providing the raw materials to make new stars.
You might also like...
Image Credits:
lagoon nebula background image, courtesy of NASA, ESA, and STScI; Earth and Sun, courtesy of NASA; Mars, courtesy of NASA/Greg Shirah; Neptune, courtesy of NASA/JPL; Uranus, courtesy of NASA/JPL; visible Universe, NASA/ESA/S. Beckwith(STScI) and The HUDF Team; bootprint on the Moon, courtesy of NASA; Milky Way over Thailand, © Matipon Tangmatitham; Comet ISON, Courtesy of Mike Hankey via NASA; Colors of Mercury, courtesy of NASA / JHU Applied Physics Lab / Carnegie Inst. Washington; Milky Way Galaxy, © AMNH; massive dying star, © AMNH.



 Biodiversity
Biodiversity
 Brain
Brain
 Genetics
Genetics
 Marine BiOLogy
Marine BiOLogy
 MicrobiOLogy
MicrobiOLogy
 PaleontOLogy
PaleontOLogy
 ZoOLogy
ZoOLogy
 AnthropOLogy
AnthropOLogy
 ArchaeOLogy
ArchaeOLogy
 Astronomy
Astronomy
 Climate Change
Climate Change
 Earth
Earth
 Physics
Physics
 Water
Water

