Work the System

We often think of the oceans as one big bowl of salt water. But the oceans have lots of different kinds of environments. In fact, there are more kinds of environments in the ocean than on land!
Coral reefs , estuaries , continental shelves , the deep sea ... these are some of the ecosystems within the oceans. Ecosystems are communities of organisms that depend on each other and their surroundings. Each ecosystem is connected to those around it.
Too Many Examples? SAMPLE!
When I investigate an ecosystem, the first thing I need to find out is what lives there. I want to know how many different species, or kinds, of plants and animals live in the ecosystem. I also want to know how many individuals of each species live there.
Of course, I can’t count every living thing! So instead, I take several samples to try to figure out how many of each species of plant and animal live across the entire ecosystem. This is called sampling.
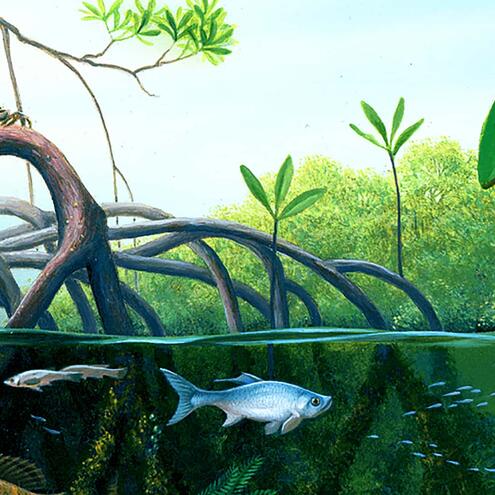
Explore this mangrove ecosystem.
- Pick an area to sample. Click on a box to sample that part of the mangrove swamp.
- Count the number of species. How many different kinds of plants and animals do you see?
- Repeat steps 1 and 2. How many other species do you see?
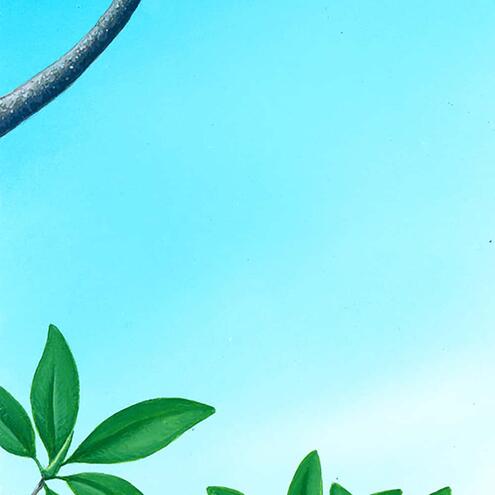


How many different species do you see?
3
5
1

red mangrove
(Rhizopora mangle)
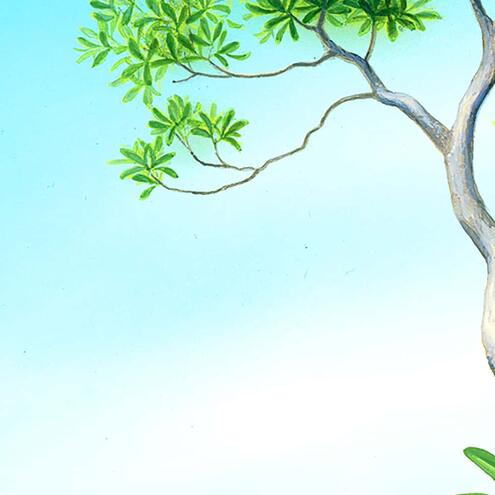

How many different species do you see?
2
1
6

red mangrove
(Rhizopora mangle)

How many different species do you see?
4
5
2

red mangrove
(Rhizopora mangle)

snowy egret
(Egretta thula)
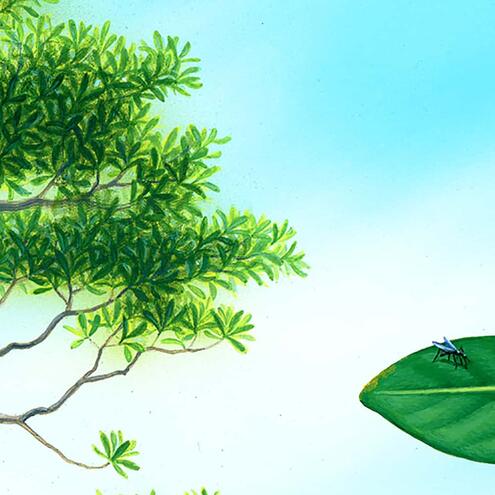

How many different species do you see?
1
2
5

red mangrove
(Rhizopora mangle)

mosquito
(Anopheles)
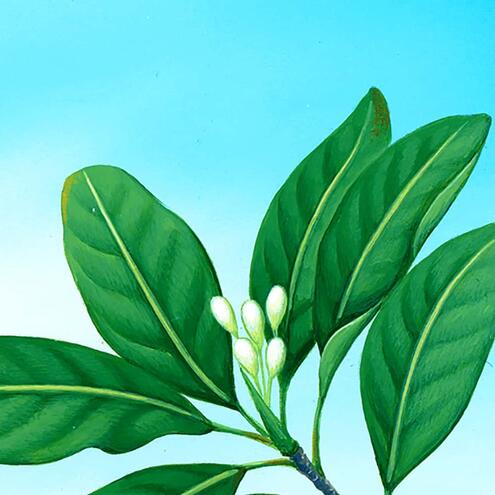

How many different species do you see?
1
2
4

red mangrove
(Rhizopora mangle)
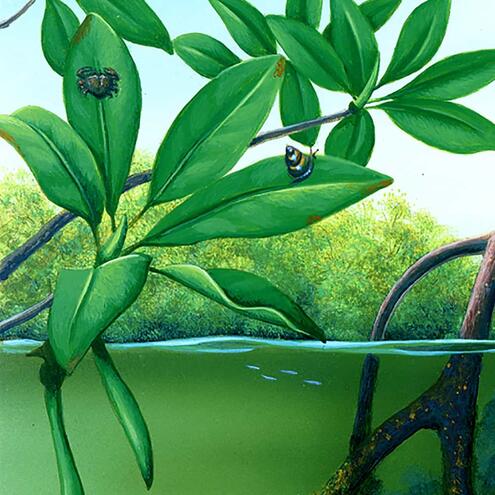

How many different species do you see?
3
8
5

red mangrove
(Rhizopora mangle)

periwinkle snail
(Littoraria angulifera)

mangrove gambusia
(Gambusia rhizophorae)
red algae
(Bostrychia montagnei)

mangrove tree crab
(Aratus pisoni)
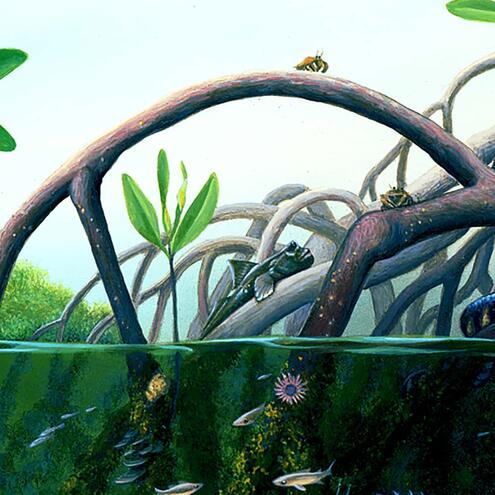

How many different species do you see?
11
9
14

red mangrove prop roots
(Rhizopora mangle)

mangrove snake
(Nerodia clarkii compressicauda)

mangrove tree crab
(Aratus pisoni)

mangrove gambusia
(Gambusia rhizophorae)

juvenile common snook
(Centropomus undecimalis)

variegated feather duster worms
(Bispira variegata)

common mudskipper
(Periophthalmus kalolo)

flat tree-oysters
(Isognomon alatus)

orange lumpy encrusting sponge
(Ulosa ruetzleri)

mermaid's wineglass
(Acetabularia calyculus)

red algae
(Bostrychia montagnei)
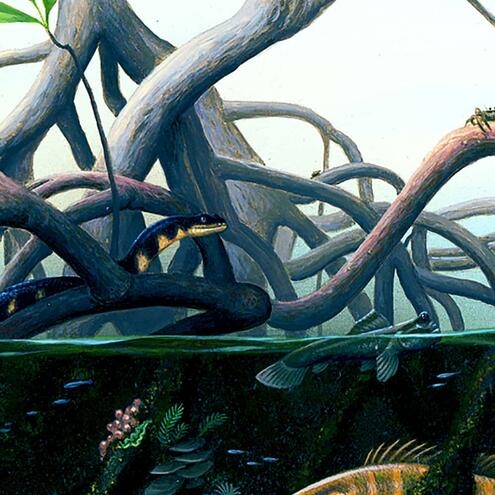

How many different species do you see?
12
9
16

red mangrove prop roots
(Rhizopora mangle)

mangrove snake
(Nerodia clarkii compressicauda)

mangrove tree crab
(Aratus pisoni)

mangrove gambusia
(Gambusia rhizophorae)

grey snapper
(Lutjanus griseus)
mangrove tunicates
(Ecteinascidia turbinata)

variegated feather duster worms
(Bispira variegata)

common mudskipper
(Periophthalmus kalolo)

flat tree-oysters
(Isognomon alatus)
lettuce slug
(Elysia crispata)

green algae
(Caulerpa sertularioides)

red algae
(Bostrychia montagnei)

How many different species do you see?
9
6
14

red mangrove prop roots
(Rhizopora mangle)

mangrove tree crab
(Aratus pisoni)

juvenile tarpon
(Megalops atlanticus)

mangrove gambusia
(Gambusia rhizophorae)

grey snapper
(Lutjanus griseus)

juvenile common snook
(Centropomus undecimalis)
green bubble algae
(Ventricaria ventricosa)

green algae
(Caulerpa sertularioides)

red algae
(Bostrychia montagnei)
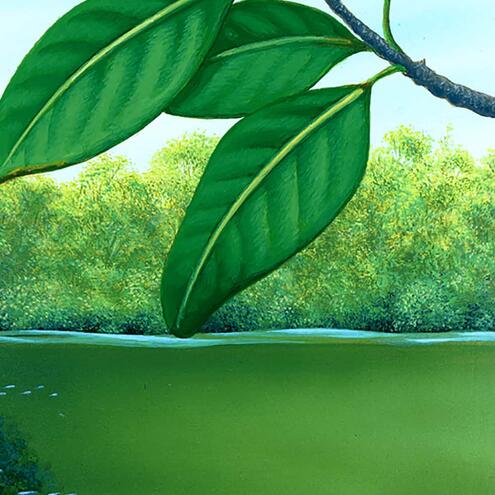

How many different species do you see?
2
1
4

red mangrove
(Rhizopora mangle)

mangrove gambusia
(Gambusia rhizophorae)
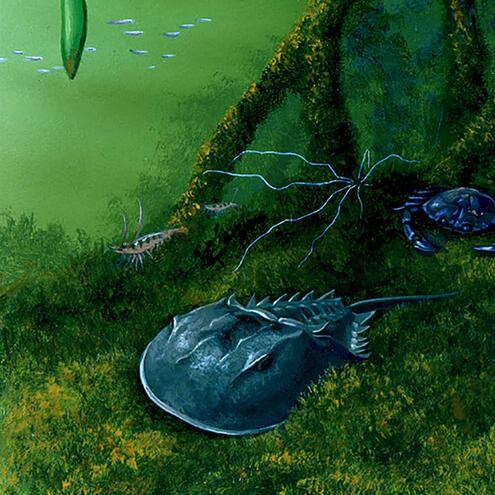

How many different species do you see?
9
10
7

red mangrove prop roots
(Rhizopora mangle)

stone crab
(Menippe mercenaria)

spaghetti worm
(Eupolymnia nebulosa)

pink shrimp
(Paneus duorarum)

horseshoe crab
(Limulus polyphemus)

mangrove gambusia
(Gambusia rhizophorae)

red algae
(Bostrychia montagnei)

How many different species do you see?
16
12
9

red mangrove propagules
(Rhizopora mangle)

red algae
(Bostrychia montagnei)

blue crab
(Callinectes sapidus)

stone crab
(Menippe mercenaria)

pink shrimp
(Paneus duorarum)

sheepshead seabream
(Archosargus probatocephalus)

beaugregory damselfish
(Stegastes leucostictus)

juvenile common snook
(Centropomus undecimalis)

variegated feather duster worms
(Bispira variegata)

flat tree-oysters
(Isognomon alatus)

mermaid's wineglass
(Acetabularia calyculus)

green algae
(Caulerpa sertularioides)

How many different species do you see?
13
16
8

red mangrove prop roots
(Rhizopora mangle)

red algae
(Bostrychia montagnei)

grey snapper
(Lutjanus griseus)

juvenile grey snapper
(Lutjanus griseus)

juvenile common snook
(Centropomus undecimalis)

mangrove tunicates
(Ecteinascidia turbinata)

variegated feather duster worms
(Bispira variegata)

spiny lobster
(Panulirus argus)

flat tree-oysters
(Isognomon alatus)

orange lumpy encrusting sponge
(Ulosa ruetzleri)

mermaid's wineglass
(Acetabularia calyculus)

green bubble algae
(Ventricaria ventricosa)

green algae
(Caulerpa sertularioides)
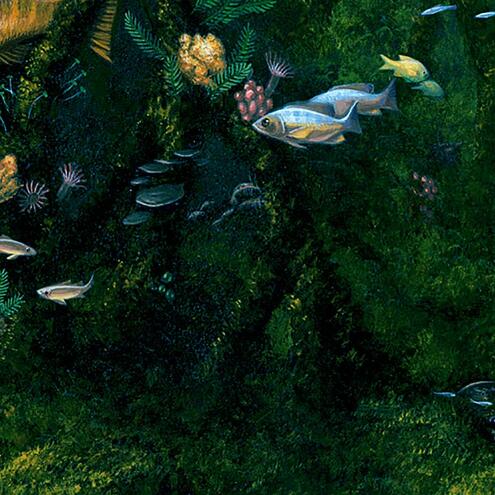

How many different species do you see?
19
13
16

red mangrove prop roots
(Rhizopora mangle)

red algae
(Bostrychia montagnei)

mud crab
(Panopeus sp.)

pink shrimp
(Paneus duorarum)

mangrove gambusia
(Gambusia rhizophorae)

beaugregory damselfish
(Stegastes leucostictus)

grey snapper
(Lutjanus griseus)

juvenile grey snapper
(Lutjanus griseus)

juvenile common snook
(Centropomus undecimalis)

mangrove tunicates
(Ecteinascidia turbinata)

variegated feather duster worms
(Bispira variegata)

flat tree-oysters
(Isognomon alatus)

orange lumpy encrusting sponge
(Ulosa ruetzleri)

mermaid's wineglass
(Acetabularia calyculus)

green bubble algae
(Ventricaria ventricosa)

green algae
(Caulerpa sertularioides)
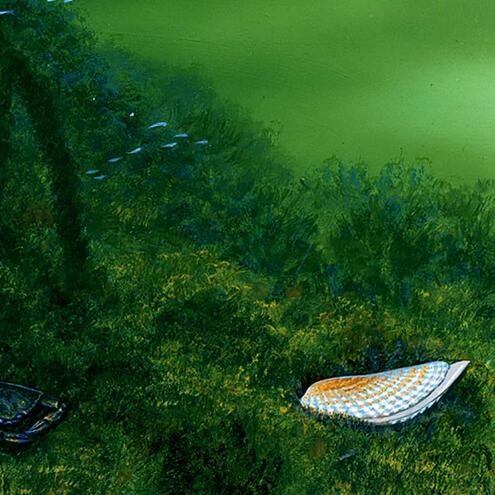

How many different species do you see?
5
7
2

red mangrove prop roots
(Rhizopora mangle)

red algae
(Bostrychia montagnei)

mud crab
(Panopeus sp.)

angelwing clam
(Cyrtopleura costata)

mangrove gambusia
(Gambusia rhizophorae)
A Sea of Questions ? ? ?
What kinds of questions do scientists ask when they study an ocean ecosystem? Good question! Scroll down this page to see some questions I asked about a tropical mangrove ecosystem.

How do mangroves interact with other ecosystems?
Many young fish find shelter in the mangrove forests until they grow up and move to deeper waters. The roots provide places to hide from their enemies.
What makes the mangrove different from other ecosystems?
The mangrove ecosystem is a special forest found in warm, coastal regions. The trees take root in the ocean while their leaves stay above water. This makes them the perfect home for both land and marine plants and animals!
How have mangrove trees adapted to live in salt water?
Mangrove trees live in water that's 10 times saltier than that which would kill most other land plants. Why? Their roots filter most of the salt out of the seawater.
Are mangroves endangered ecosystems?
Mangroves are among the most threatened habitats in the world. More than half of the original mangrove forests have been lost and the remaining forests are damaged.
ANY QUESTIONS?
Now that you've explored some of the questions scientists ask, investigate another ocean ecosystem, and ask:
- How are organisms within the ecosystem important to one another?
- What makes this ecosystem special?
- How do organisms adapt to living in this ecosystem?
- How is this ecosystem connected to neighboring ones?
- Is this ecosystem endangered?
Image Credits:
Photos: A Sea of Questions: Ian Harrison: courtesy of AMNH, Denis Finnin Mangrove: courtesy of OAR, National Undersea Research Program; Too many examples? Sample! Ian Harrison: courtesy of AMNH, Denis Finnin; Illustrations: Russell Farrell



 Biodiversity
Biodiversity
 Brain
Brain
 Genetics
Genetics
 Marine BiOLogy
Marine BiOLogy
 MicrobiOLogy
MicrobiOLogy
 PaleontOLogy
PaleontOLogy
 ZoOLogy
ZoOLogy
 AnthropOLogy
AnthropOLogy
 ArchaeOLogy
ArchaeOLogy
 Astronomy
Astronomy
 Climate Change
Climate Change
 Earth
Earth
 Physics
Physics
 Water
Water

