The Milky Way Galaxy
Did you know that our star, the Sun, is just one of hundreds of billions of stars swirling within an enormous cosmic place called the Milky Way Galaxy? The Milky Way is a huge collection of stars, dust and gas. It’s called a spiral galaxy because if you could view it from the top or bottom, it would look like a spinning pinwheel. The Sun is located on one of the spiral arms, about 25,000 light-years away from the center of the galaxy. Even if you could travel at the speed of light (300,000 kilometers, or 186,000 miles, per second), it would take you about 25,000 years to reach the middle of the Milky Way.
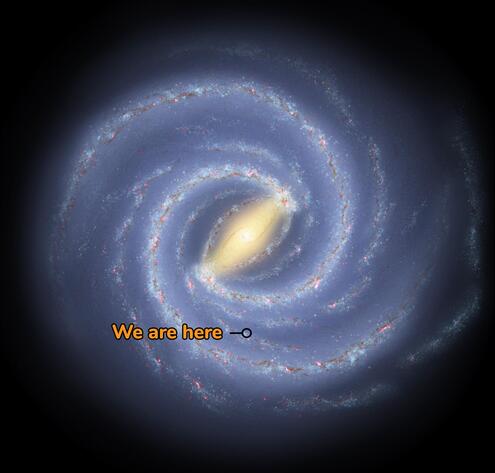

If we could travel outside our galaxy and look back, this is what our Milky Way Galaxy might look like from above. An artist created this illustration using data collected by astronomers.
Did you know that our star, the Sun, is just one of hundreds of billions of stars swirling within an enormous cosmic place called the Milky Way Galaxy? The Milky Way is a huge collection of stars, dust and gas. It’s called a spiral galaxy because if you could view it from the top or bottom, it would look like a spinning pinwheel. The Sun is located on one of the spiral arms, about 25,000 light-years away from the center of the galaxy. Even if you could travel at the speed of light (300,000 kilometers, or 186,000 miles, per second), it would take you about 25,000 years to reach the middle of the Milky Way.

If we could travel outside our galaxy and look back, this is what our Milky Way Galaxy might look like from above. An artist created this illustration using data collected by astronomers.
The Milky Way gets its name from a Greek myth about the goddess Hera who sprayed milk across the sky. In other parts of the world, our galaxy goes by other names. In China it’s called the “Silver River,” and in the Kalahari Desert in Southern Africa, it’s called the “Backbone of Night.”

This is what the Milky Way Galaxy looks like from Earth. Have you seen it in the night sky?
If you could see our galaxy from the side, it would look like a huge, thin disk with a slight bump in the center. This flat shape is caused by the galaxy spinning around. Everything in our spinning galaxy would fly off into space if it weren’t for the force of gravity.
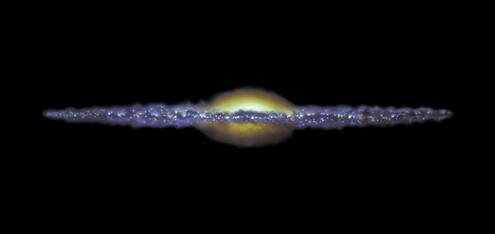
This is what the Milky Way might look like from the side. It's like a giant disk with a bump in the middle!
Without a telescope , we can see about 6,000 stars from Earth. That may seem like a lot of stars, but it’s actually only a small part of the whole. If you think of the entire galaxy as a giant pizza, all the stars you can see from Earth fall within about one pepperoni on that pizza. In fact, for every star you can see, there are more than 20 million you cannot see. Most of the stars are too faint, too far away or blocked by clouds of cosmic dust.
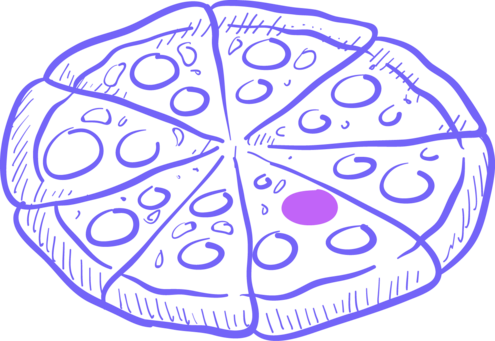
Imagine if the Milky Way Galaxy is a pepperoni pizza. All the stars that we can see from Earth are only within one pepperoni!

Q&A with Astronomer Julianne Dalcanton
Are all galaxies like the Milky Way?
No. Galaxies come in lots of different sizes. Smaller ones have millions of stars, while bigger ones contain billions. Galaxies also have different shapes. Some are spiral galaxies, like the Milky Way. Some are egg-shaped elliptical galaxies, and the rest are called irregular galaxies.
What’s your favorite galaxy, and why?
I’m fond of the “Sombrero Galaxy” because it shows how “3-D” galaxies are. Most galaxies look like flat paintings in the sky, but with the Sombrero, you really get the impression that it’s this big THING sitting out there in space!

The Sombrero Galaxy.
Is it fun being an astronomer?
Definitely. I often travel to interesting places like Hawaii and Chile. That’s because the best telescopes in the world are located on high mountains in remote places, where it’s dry and dark at night. When I need to study stars all night, I sometimes have to blast music to stay awake.

A mountaintop is a great location for an observatory. With less light and air pollution, it's much easier to observe the starry night sky with a telescope.
Image Credits:
Lake with Milky Way view, teredura58 via Flickr CC BY-NC-SA 2.0; Space background, ©Vecteezy; Milky Way Topview, Spitzer Space Telescope/NASA/JPL-Caltech/R. Hurt; Photo by Rodrigo Soares on Unsplash; Sideview of Milky Way, ©Paternstro; Pizza, Pngfuel.com; Photo of Julianne Dalcanton, courtesy of Julianne Dalcanton; Bode's Galaxy, NASA/Roberto Colombari; ESO 325-G004, NASA/ESA/Hubble; Antennae galaxies, NASA/ESA/Hubble; Sombrero galaxy, Processing Planetary Images & Enhancements For Fun CC BY-SA 2.0; Photo by Conner Baker on Unsplash.



 Biodiversity
Biodiversity
 Brain
Brain
 Genetics
Genetics
 Marine BiOLogy
Marine BiOLogy
 MicrobiOLogy
MicrobiOLogy
 PaleontOLogy
PaleontOLogy
 ZoOLogy
ZoOLogy
 AnthropOLogy
AnthropOLogy
 ArchaeOLogy
ArchaeOLogy
 Astronomy
Astronomy
 Climate Change
Climate Change
 Earth
Earth
 Physics
Physics
 Water
Water






