Consequences of Warming
Part of Hall of Planet Earth.
Change is already visible. Severe droughts, storms and heat waves are becoming more common. Global sea level is rising as the ocean warms and ice sheets melt, leading to more coastal floods. Climate is changing and we are seeing the consequences.
How Do Impacts Progress?
Some consequences of climate change are visible now, and more are developing over time and as warming increases. Without major CO2 reductions, rising temperatures may trigger severe impacts. What could this mean over the next 100 years?
Fingerprints of Climate Change
Because climate change can be gradual and influenced by natural as well as human causes, it is difficult to say whether a particular event was “caused” by human-induced climate change. But we can examine how the likelihood of an extreme event changes. Heat waves like the one in Europe in 2003, responsible for as many as 70,000 deaths, were rare during the last century. Unabated warming increases the odds that summers could regularly become as hot as the summer of 2003.
Arkaprava Ghosh/Barcroft India via Getty Images
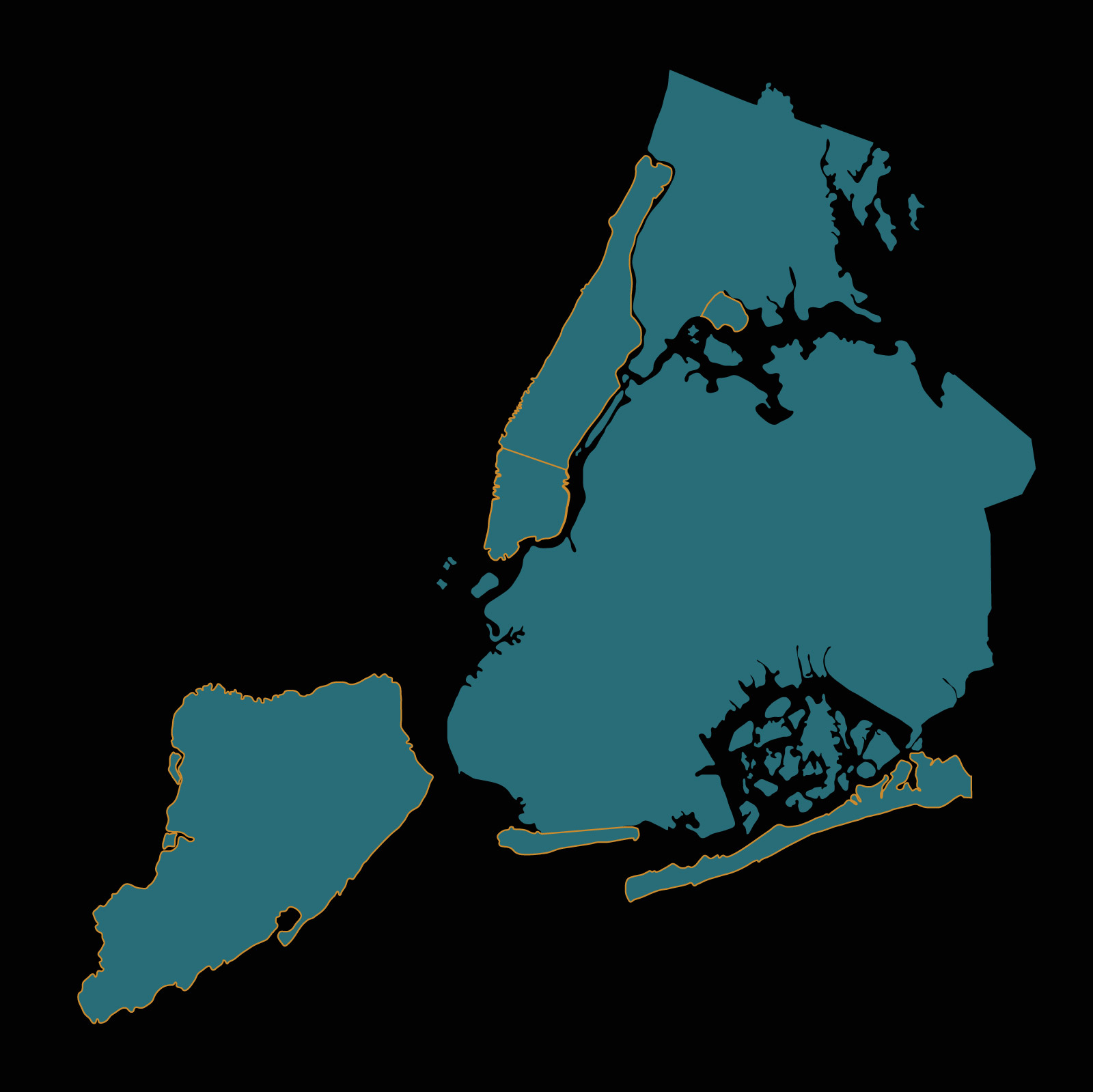
Interactive: Climate Change in New York City
Downtown Manhattan
Shoring up subways
In over 150 cities, people rely on underground transportation. With more extreme weather, subway infrastructure is increasingly vulnerable to flooding.
The MTA is preparing by flood-proofing New York City’s subway system.
Rockaway, Queens
Preparing for power loss
As the climate warms, intense storms are becoming more common, placing power grids at risk.
Creative use of sunlight can reduce energy demand and help keep cities running during power outages.
Cosney Island, Brooklyn
Making housing resilient
Around the world, climate change is expected to affect poor communities disproportionately.
In New York City, public housing is being redesigned to better withstand extreme weather events.
New York and other cities are developing strategies to address the impacts of warming
Why Are Seas Rising?
Globally, average sea level rose 21 centimeters (8.2 inches) between 1880 and 2009. Why? Water takes up more space as it warms, causing oceans to expand. In addition, mountain glaciers have melted, adding water from the land to the sea. The great ice sheets on Greenland and Antarctica are also shrinking rapidly, which suggests that over the next 100 years, sea level rise will take place even faster than in the 1900s.
Shutterstock
Climate Change and Risk
We can see that climate is changing, but specific consequences are still unknown—for example, precisely how much sea level will rise. This means climate change presents risks that are uncertain, but potentially devastating. Efforts to curb emissions and adapt to a rapidly changing climate can help safeguard society against this uncertain future.
Yearly odds of an extreme heat wave in Europe
Past Events and Future Risk
Natural changes in climate can also have severe consequences. In the late 1500s, a cool period known as the Little Ice Age began in the Northern Hemisphere. The 1600s, when temperatures were at their lowest, was marked by famine, migration and conflict. Today it is warming, not cooling, that threatens food production and could increase the risk of widespread strife.
 Illustration from 1627 depicting strife during the Thirty Years’ War (1618–1648)
Illustration from 1627 depicting strife during the Thirty Years’ War (1618–1648)Pictorial Press/Alamy
Extreme Weather
As warming progresses, severe weather events that were once rare, such as heat waves, droughts and floods, will become more common. What’s more, the most extreme events of the future will be considerably more severe than they are today, posing serious risks to society.
 Drought-damaged corn. Indiana, 2012
Drought-damaged corn. Indiana, 2012Indiana Stock/Alamy
Next Steps
The most dire consequences of climate change are not inevitable. Society can make choices now that reduce the chances of catastrophe in the future. Cutting CO2 emissions lessens the likelihood of some of the gravest potential consequences. Preparing infrastructure for sea-level rise and extreme heat now can help people and communities manage immediate impacts.