Our Warming World
Part of Hall of Planet Earth.
The recent rise in global temperature has been observed in long-term measurements of the atmosphere and oceans. Current climate change--and its unusually rapid rate--is not apparent in one day or year. But over decades, an unmistakable warming trend becomes clear.
What Makes a Trend
Evidence for climate change is not based on measurements from a single year or place. Many decades of data from instruments across the globe reveal an accelerated warming trend since the 1970s.
 Shutterstock
Shutterstock
Tracking Modern Temperature
The Central England Temperature record dates back to 1659, making it the longest running temperature record in the world. Measurements from a single station may not reflect overall regional climate, so scientists use instruments spread throughout central England for the record. It is still updated daily by the UK Meteorological Office.
Thermometer, Museo Galileo; Weather monitoring satellite, Shutterstock.
What’s Happening to the Arctic?
The warming observed globally is magnified in the Arctic. While worldwide average temperature climbed about 1°C (1.8°F) since 1900, the Arctic warmed by 1.6°C (2.9°F) over the same period. This is partly connected to the loss of sea ice and snow cover, which reduces how much sunlight is reflected off ocean and land surfaces. Warming threatens Arctic peoples’ livelihoods and endangers fragile ecosystems.
Increase in average temperature since 1900:
Causes of Global Warming
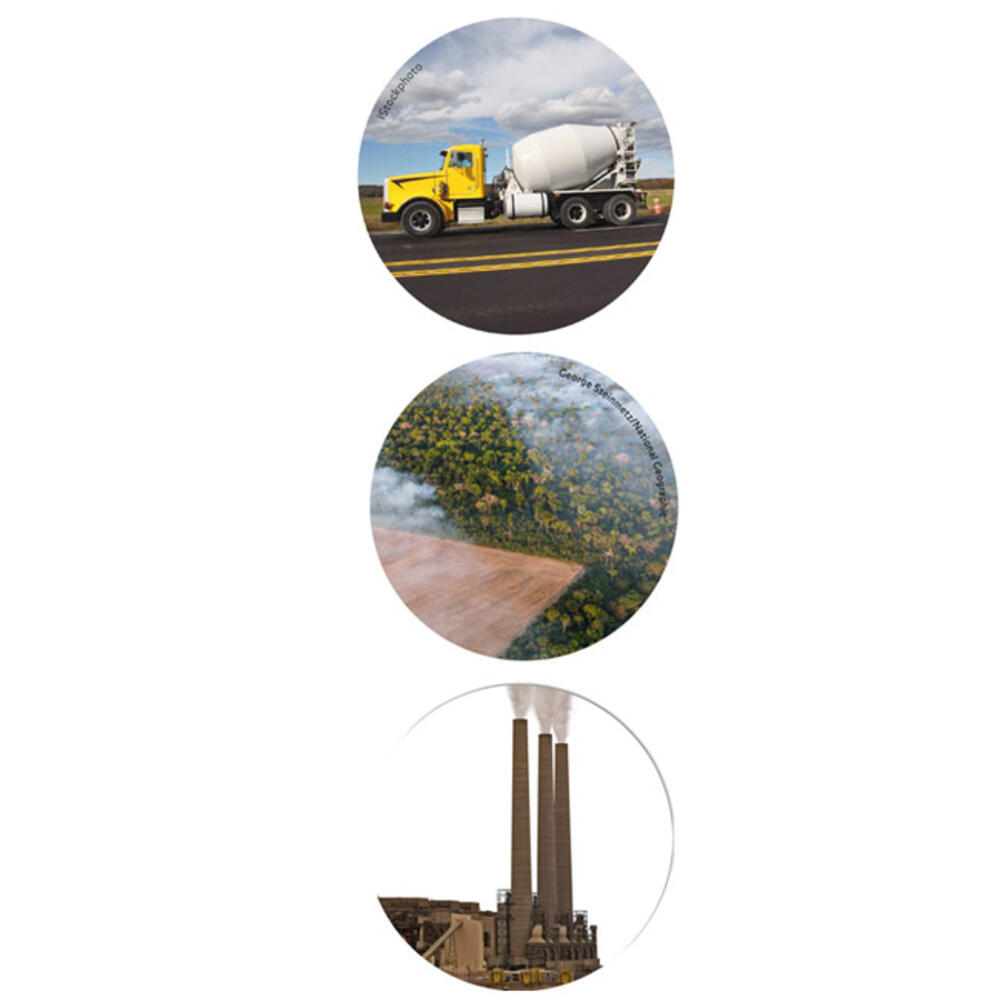
Human activity is warming the planet. Since the use of coal, oil and gas became widespread after 1750, humans have added about 2,040 billion metric tons (Human CO2 emissions, 1750–2011: 2,040 ± 310 gigatons) of heat-trapping carbon dioxide to the atmosphere, where it can linger for thousands of years. While burning fossil fuels is the main driver of warming, deforestation and cement production also contribute. The effects of rapid warming vary from region to region, but all of Earth’s systems are affected by climate change.
Cement Production: Raw materials used for making cement release CO2 during the production process.Forestry and Agriculture: Agriculture and loss of the world’s forests produce significant CO2 emissions.Fossil Fuels: Most CO2 emissions are from burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil and natural gas for producing electricity and heat, as well as for industrial processes and transportation

Natural Factors
Climate varies naturally, so how can we distinguish between natural climate drivers and human causes? Many natural factors affecting climate, such as volcanic eruptions and changes in solar energy, are well understood—and they simply cannot account for the warming we see today. The only factor that explains the timing and magnitude of current warming is the impact of greenhouse gases released by human activity.
Eruption, StockTrek/AGE Fotostock; Sun, StockTrek/Alamy.
The CO2 released today can stay in the atmosphere for thousands of years.
Fossil fuels form over several hundred million years from the carbon in deeply buried remains of organisms. Burning these fuels releases carbon into the atmosphere as CO2 in just minutes. Living things, oceans and rocks can remove CO2 from the atmosphere, but not quickly enough to balance fossil fuel emissions.
Our Changing Atmosphere
The level of CO2 in the atmosphere is higher than it has been in at least 800,000 years, and possibly the last three million years.